

With the increasing awareness of skin health, protecting your skin from the sun’s harmful rays has never been more important. Sunscreen and its Sun Protection Factor (SPF) are crucial components of any skincare routine, regardless of the season. This article will delve into what SPF is, how sunscreen works, the different types available, and tips on choosing and using the right sunscreen for your needs.
What is SPF?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor, a measure of how well a sunscreen can protect your skin from UVB rays, the kind of radiation that causes sunburn, damages skin, and can contribute to skin cancer. The SPF number indicates how long you can stay in the sun without getting burned compared to no protection.
How Sunscreen Works
Sunscreen protects your skin by either absorbing or reflecting UV radiation. There are two main types of UV rays to be aware of:
- UVA Rays: Penetrate deep into the skin and are responsible for premature aging and wrinkles (photoaging). They can also contribute to skin cancer.
- UVB Rays: Affect the surface of the skin and are the main cause of sunburn. They play a significant role in developing skin cancer.
Chemical vs. Physical Sunscreen
Sunscreens can be broadly classified into two categories: chemical (organic) and physical (inorganic) sunscreens.
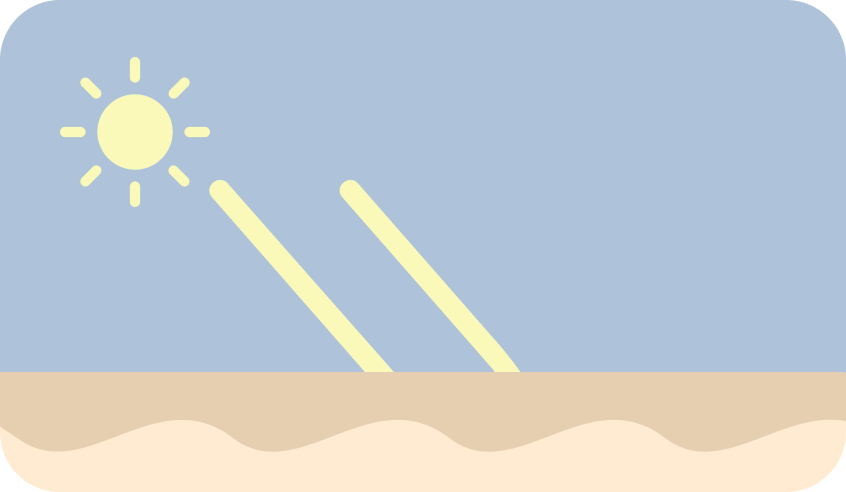

Chemical Sunscreen
- How It Works: Absorbs UV radiation and converts it into heat, which is then released from the skin.
- Common Ingredients: Oxybenzone, avobenzone, octisalate, octocrylene, homosalate, and octinoxate
- Pros: Lightweight, less visible on the skin, and often more water-resistant.
- Cons: Can cause skin irritation and allergic reactions in some people. Requires 20 minutes to become effective after application.
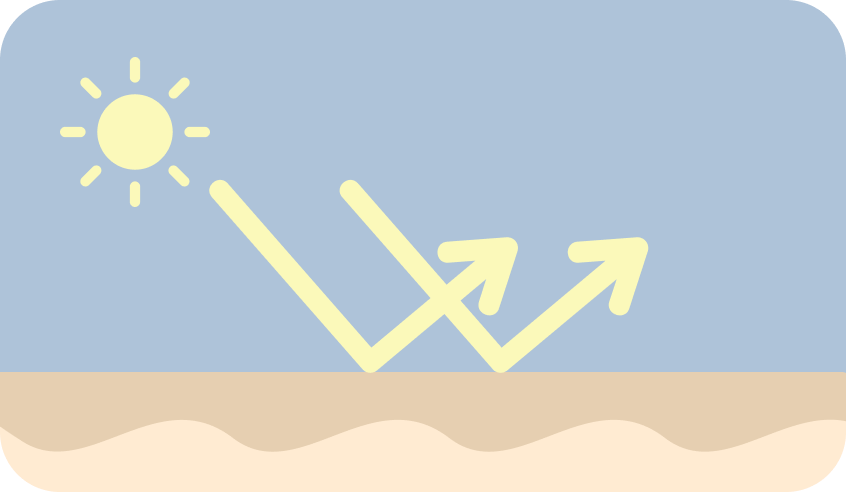

Physical Sunscreen
- How It Works: Sits on top of the skin and reflects UV radiation.
- Common Ingredients: Zinc oxide and titanium dioxide.
- Pros: Provides immediate protection, less likely to cause skin irritation, and offers broad-spectrum protection.
- Cons: Can be thicker and leave a white cast on the skin, especially on darker skin tones.
Choosing the Right SPF
The American Academy of Dermatology recommends using a sunscreen with at least SPF 30, which blocks 97% of UVB rays. Higher SPF values provide slightly more protection, but no sunscreen can block 100% of UVB rays. It’s essential to apply sunscreen correctly and reapply it every two hours, or more frequently if you’re swimming or sweating.
Get Your Sun Protection at Rexall
Incorporating sunscreen into your daily skincare routine is a simple yet effective way to protect your skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. By understanding the importance of SPF, choosing the right sunscreen, and applying it correctly, you can enjoy the outdoors while keeping your skin healthy and youthful. Remember, the best sunscreen is the one you’ll use consistently, so find a formula you love and make it a part of your daily habit. Your skin will thank you!







