Vaccines
Rexall Pharmacists are injection certified and can administer a wide range of vaccines including the flu, Hepatitis A and B and COVID-19 vaccines, to support your overall health and wellness. Vaccine availability and administration may vary based on province. Speak with your Rexall Pharmacist to determine which vaccines may be right for you.
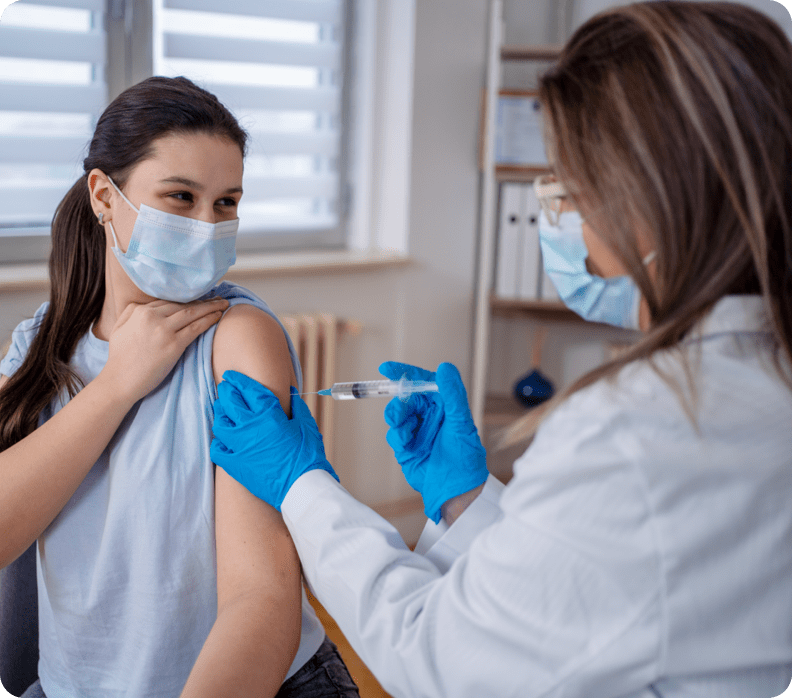



Travel Vaccines
Travelling to a destination outside of Canada? Rexall Pharmacists can administer a wide range of travel vaccines to help you be prepared. They can also provide helpful advice on essential over-the-counter travel medications and products. Speak with your Rexall Pharmacist today.
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centers
You can receive the Yellow Fever Vaccine at the following Rexall locations:
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centers
You can receive the Yellow Fever Vaccine at the following Rexall locations:
Alberta
Wye & Ash, Sherwood Park
301 Wye Road, Suite 11
Sherwood Park, AB T8B 0A4
Store #7234
Phone Number:
Ellerslie & Parsons
9404 Ellerslie Rd
SW Edmonton, AB T6X 0K6
Store #7232
Phone Number:
Ontario
Duckworth Street Barrie
353 Duckworth Street
Barrie, ON L4M 3X8
Store #1370
Phone Number:
Brightwater
2-175 Lakeshore Road West
Mississauga, ON L5H 0A6
Store #8223
Phone Number:
Stone Church/Upper Ottawa Hamilton
1395 Upper Ottawa Street
Hamilton, ON L8W 3L5
Store #204
Phone Number:
College Square Nepean
31363B Woodroffe Avenue
Nepean, ON K2G 1V7
Store #1149
Phone Number:
British Columbia
Village Sq Whistler
201-4204 Village Square
Whistler, BC V8E 1H5
Store #7116
Phone Number:
Travel Vaccines
Planning on travelling? Need travel vaccinations? Rexall Pharmacists can help inform you about the requirements for each vaccine.
Hepatitis A is a viral infection of the liver that’s caused by exposure to infected feces, often by consuming contaminated food or water.33 Infections are common in areas like Africa, India, and South America.33
Hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for travellers who are 6 months of age and older.34 It usually consists of a primary dose and a booster dose given at least 6 months apart.34 Consider getting vaccinated with your first dose at least 2 weeks before travelling.34,35 No additional doses beyond the recommended 2 doses are needed.34
Hepatitis B is a type of viral liver infection that spreads through infected blood and body fluids.10 High risk areas for infections include Asia and Africa.10
Hepatitis B vaccinations are routinely given to infants and children.11 The number of recommended doses will vary based on several factors; ask your pharmacist to learn more.11 If you’re an unvaccinated adult, it requires 3 doses (and sometimes a booster dose), given a week to several months apart depending on your vaccine schedule.11,36,37
Consider getting vaccinated at least 1 month before travelling.38 There are vaccines available that protect you against both hepatitis A and hepatitis B.36
Travellers’ diarrhea (Montezuma’s revenge, Delhi belly) is a type of illness that’s caused by bacteria, parasites, or viruses after consuming contaminated food or water.39 Cholera is a type of intestinal infection that’s caused by a type of bacteria called Vibrio cholerae, also usually because of consuming contaminated food or water.40 High risk areas common to both illnesses include Central and South America, Africa, and Asia.39,40
For adults and children who are 6 years of age and older, vaccination against cholera and travellers’ diarrhea for the first time requires 2 doses and should be considered at least 2 weeks before travelling.41 For children between the ages of 2 and 6 years, first-time vaccination requires 3 doses, and should be considered at least 3 weeks before travelling.41 Regardless of your age, you should get your last dose at least 1 week before travelling. Booster doses may be recommended depending on when you were last immunized.41
All vaccines shown are available in all provinces, though the prescription and administration of the vaccines can vary. Speak with your Rexall Pharmacist and we will work with your physician to ger prescriptions as required.
To learn more about which vaccines are required by destination, please visit https://travel.gc.ca/travelling/health-safety/vaccines.
Speak with your Rexall Pharmacist for a review on unique vaccine requirements by destination.
*Some vaccines require a prescription to be administered. Speak with your Rexall pharmacist and we will work with your physician to get prescriptions as required.
References:
- Government of Canada. Flu (influenza): Prevention and risks. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/flu-influenza/prevention-risks.html. Last updated October 20, 2021. Accessed November 8, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Canadian Immunization Guide Chapter on Influenza and Statement on Seasonal Influenza Vaccine for 2022–2023. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/vaccines-immunization/canadian-immunization-guide-statement-seasonal-influenza-vaccine-2022-2023.html. Last updated October 14, 2022. Accessed November 23, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. COVID-19: Main modes of transmission. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/2019-novel-coronavirus-infection/health-professionals/main-modes-transmission.html. Last updated June 29, 2021. Accessed November 8, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. COVID-19 vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-26-covid-19-vaccine.html. Last updated November 18, 2022. Accessed November 23, 2022.
-
Immunize BC. Pneumococcal Disease. https://immunizebc.ca/pneumococcal. Last updated August 25, 2022. Accessed November 8, 2022.
-
BC Centre for Disease Control. Pneumococcal. http://www.bccdc.ca/health-info/diseases-conditions/pneumococcal. Accessed November 8, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Pneumococcal vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-16-pneumococcal-vaccine.html. Last updated September 13, 2022. Accessed November 23, 2022.
-
Canadian Paediatric Society. Meningococcal disease. https://caringforkids.cps.ca/handouts/health-conditions-and-treatments/meningococcal_diseases. Last updated September 2020. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Meningococcal vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-13-meningococcal-vaccine.html. Last updated September 23, 2021. Accessed November 23, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Hepatitis B. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/hepatitis-b.html. Last updated July 27, 2021. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Hepatitis B vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-7-hepatitis-b-vaccine.html. Last updated May 20, 2022. Accessed November 23, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Poliomyelitis (Polio). https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/poliomyelitis-polio.html. Last updated September 9, 2022. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Poliomyelitis vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-17-poliomyelitis-vaccine.html. Last updated July 28, 2022. Accessed November 23, 2022.
-
BC Centre for Disease Control. Measles. http://www.bccdc.ca/health-info/diseases-conditions/measles. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
BC Centre for Disease Control. Mumps. http://www.bccdc.ca/health-info/diseases-conditions/mumps. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
BC Centre for Disease Control. Rubella. http://www.bccdc.ca/health-info/diseases-conditions/german-measles-rubella. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Measles vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-12-measles-vaccine.html. Last updated November 23, 2021. Accessed November 23, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Mumps vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-14-mumps-vaccine.html. Last updated November 23, 2021. Accessed November 23, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Rubella vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-20-rubella-vaccine.html. Last updated November 23, 2021. Accessed November 23, 2022.
-
BC Centre for Disease Control. Diphtheria. http://www.bccdc.ca/health-info/diseases-conditions/diphtheria. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
BC Centre for Disease Control. Tetanus. http://www.bccdc.ca/health-info/diseases-conditions/tetanus. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Diphtheria toxoid: Canadian Immunization Guide. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-4-diphtheria-toxoid.html. Last updated November 23, 2021. Accessed November 23, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Tetanus toxoid: Canadian Immunization Guide. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-22-tetanus-toxoid.html. Last updated November 23, 2021. Accessed November 23, 2022.
-
BC Centre for Disease Control. Haemophilus Influenzae Type B (Hib). http://www.bccdc.ca/health-info/diseases-conditions/haemophilus-influenzae-type-b-hib. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Haemophilus influenzae Type B vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-5-haemophilus-influenzae-type-b-vaccine.html. Last updated September 23, 2021. Accessed November 23, 2022.
-
BC Centre for Disease Control. Chickenpox / Varicella. http://www.bccdc.ca/health-info/diseases-conditions/chickenpox-varicella. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Varicella (chickenpox) vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-24-varicella-chickenpox-vaccine.html. Last updated November 23, 2021. Accessed November 24, 2022.
-
BC Centre for Disease Control. Shingles. http://www.bccdc.ca/health-info/diseases-conditions/shingles. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Herpes zoster (shingles) vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-8-herpes-zoster-(shingles)-vaccine.html. Last updated January 20, 2022. Accessed November 24, 2022.
-
BC Centre for Disease Control. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) / Genital Warts. http://www.bccdc.ca/health-info/diseases-conditions/human-papillomavirus-(hpv)-genital-warts. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Provincial and territorial routine and catch-up vaccination schedule for infants and children in Canada. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/provincial-territorial-immunization-information/provincial-territorial-routine-vaccination-programs-infants-children.html. Last updated July 7, 2022. Accessed November 24, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Human papillomavirus vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-9-human-papillomavirus-vaccine.html. Last updated September 23, 2021. Accessed November 24, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Hepatitis A. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/hepatitis-a.html. Last updated May 31, 2018. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Hepatitis A vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-6-hepatitis-a-vaccine.html. Last updated November 23, 2021. Accessed November 24, 2022.
-
HAVRIX® [product monograph]. Mississauga, ON: GlaxoSmithKline Inc. Retrieved from: https://pdf.hres.ca/dpd_pm/00047293.PDF. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
TWINRIX® [product monograph]. Mississauga, ON: GlaxoSmithKline Inc. Retrieved from: https://pdf.hres.ca/dpd_pm/00047291.PDF. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
ENGERIX-B® [product monograph]. Mississauga, ON: GlaxoSmithKline Inc. Retrieved from https://pdf.hres.ca/dpd_pm/00058559.PDF. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
CDC. Last-Minute Travelers. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2020/preparing-international-travelers/last-minute-travelers. Last updated November 21, 2019. Accessed November 10, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Travellers’ diarrhea. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/diarrhea.html. Last updated March 19, 2022. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
Government of Canada. Cholera. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/cholera.html. Last updated December 20, 2021. Accessed November 9, 2022.
-
Dukoral® [product monograph]. Kirkland, Québec: Valneva Canada Inc. Retrieved from: https://pdf.hres.ca/dpd_pm/00066823.PDF. Accessed November 9, 2022.