Understanding the Signs of Gum Disease & How to Avoid It


Gum disease is more common than most people think, and it's not just about your smile. When left untreated, it can lead to serious health concerns like heart disease, diabetes, and even stroke. The good news? Gum disease is both preventable and treatable, especially in its early stages. By knowing the signs, understanding the risk factors, and following a daily oral care routine, you can protect your gums, your smile, and your overall health.
At Rexall, we believe in Healthy Mouth, Healthier you—caring for your oral health is caring for your whole body.
What Does Gum Disease Look Like?
The earliest stage of gum disease starts with a buildup of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth and gums every day. If not removed through daily brushing and flossing, plaque can irritate your gums, leading to inflammation and infection. Early signs of gingivitis include:
- Sensitive teeth
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums
- Bad breath that won’t go away
However, you may not even notice the symptoms until it has advanced to periodontitis, the later stage of gingivitis, since the early symptoms are often painless.
What Causes Gum Disease?
The most common cause of gingivitis is a buildup of plaque, which is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth and gums. Proper brushing and flossing can remove plaque before it causes harm. But if left to build up, it hardens into tartar, which can't be removed at home and can begin to damage your teeth and gums.
If left untreated, gingivitis can result in a more serious condition called periodontitis, which can cause infection that leads to tooth decay, bleeding gums, and even tooth loss.

While poor oral hygiene is the leading cause of gum disease, other factors can make you more vulnerable. These include:
- Smoking: Tobacco weakens gum tissue and reduces your ability to fight infection, making smokers more prone to gum disease.
- Medications: Some medications can cause dry mouth, which reduces saliva and the natural ability to wash away plaque.
- Hormonal Changes & Pregnancy: Shifts in hormone levels (especially during pregnancy) can increase blood flow to the gums, making them more sensitive, swollen, and prone to irritation.
Can Gum Disease Cause Other Health Issues?
Your oral health impacts your overall health. When your gums are inflamed or bleeding, harmful oral bacteria can enter your bloodstream, increasing the risk for several serious health conditions.

Diabetes
High blood sugar can lead to more glucose in your saliva, which feeds the bacteria that cause plaque and gum disease. Diabetes also slows healing, making it harder to recover from gum issues. In turn, keeping your blood sugar as close to target as possible will help keep your teeth and gums healthy


Heart Disease
Inflammation and infection from gum disease may increase the risk of heart disease. Research suggests that oral bacteria can enter the bloodstream, leading to plaque buildup in the arteries and increasing the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular issues


Respiratory Infections
Several studies have shown that bacteria from gum disease can be inhaled into your lungs, resulting in respiratory conditions such as pneumonia, especially in people with weakened immune systems.
Worried about gum health?
Talk to a dental professional to understand the early signs of gum disease and what you can do to support your health.
How to Treat Gum Disease at Home
You can treat the early stages of gum disease at home by following recommendations from your dental professional, which typically include:
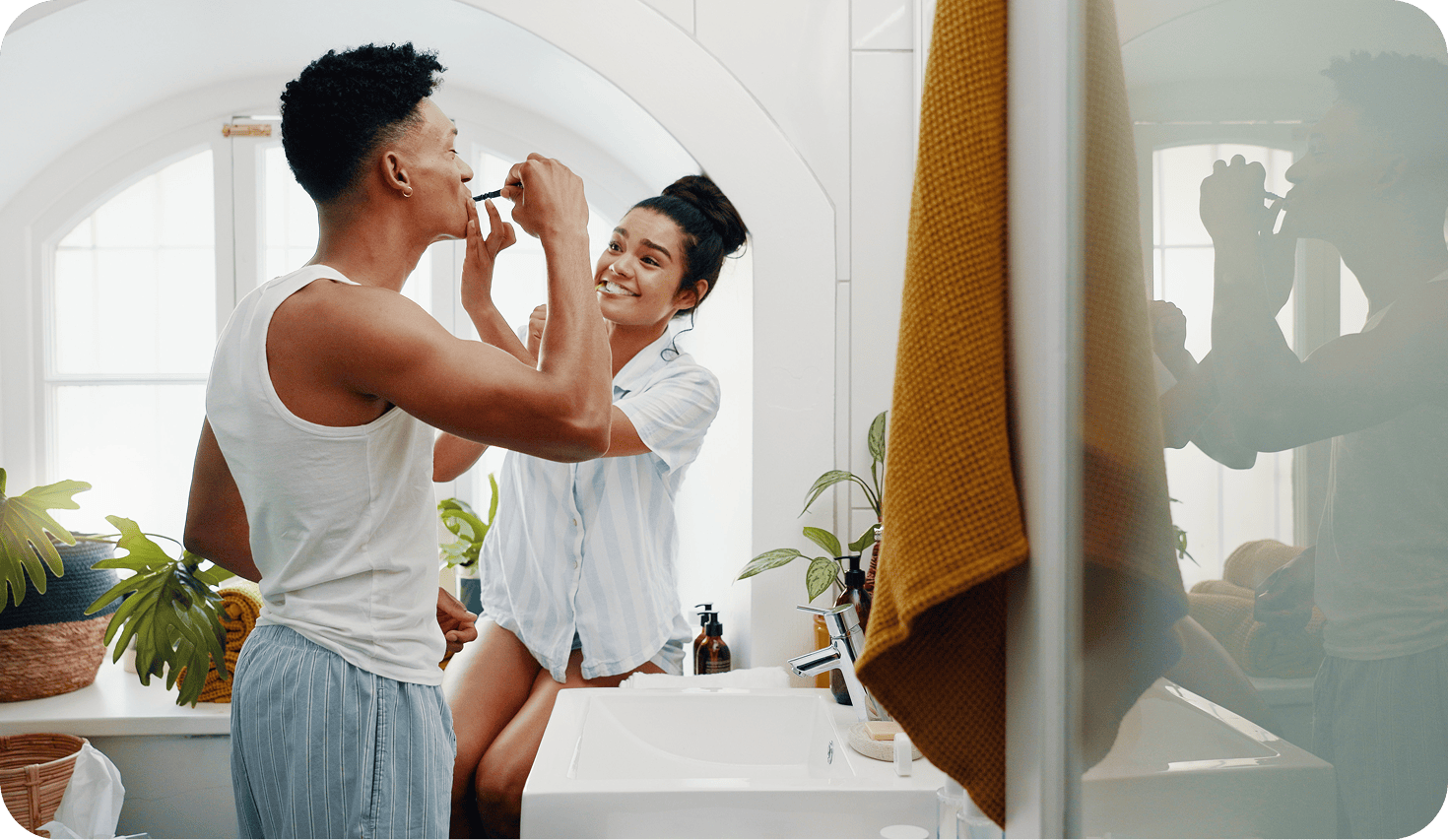


Brushing twice a day with a toothpaste that targets plaque, such as Crest Gum Detoxify
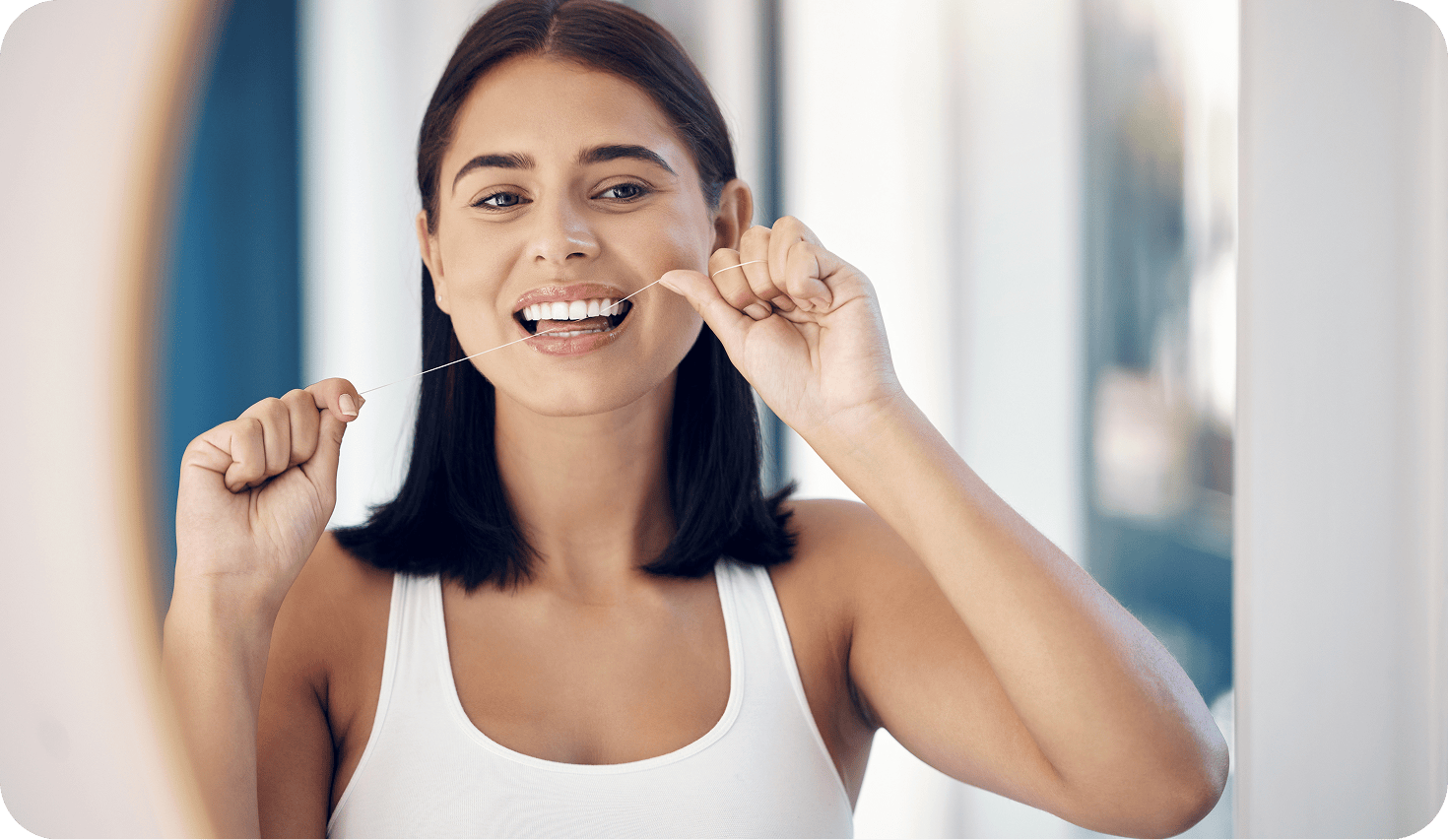


Flossing daily using string floss and pairing it with a water flosser to remove plaque below the gum line
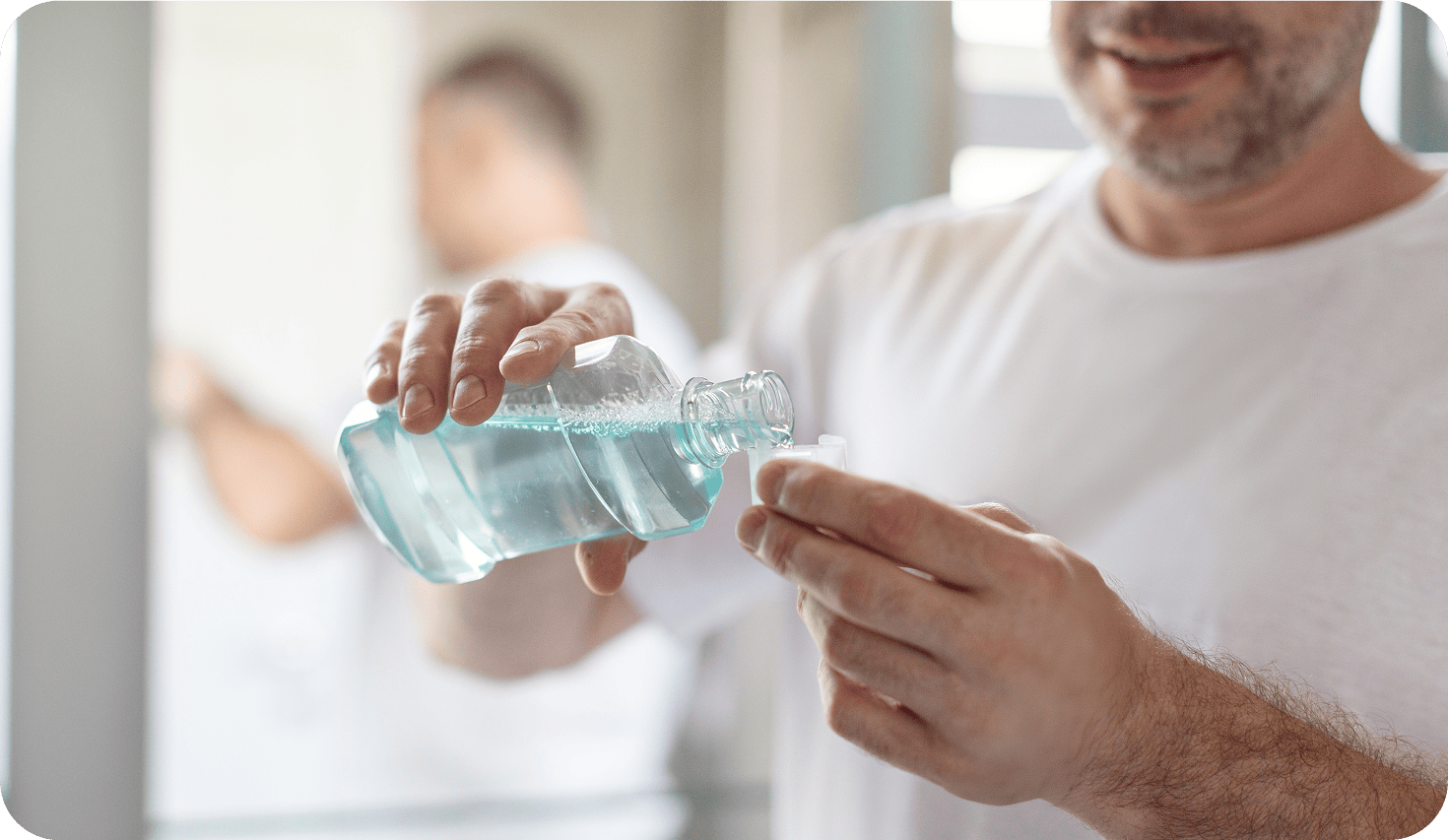


Rinsing with an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and inflammation
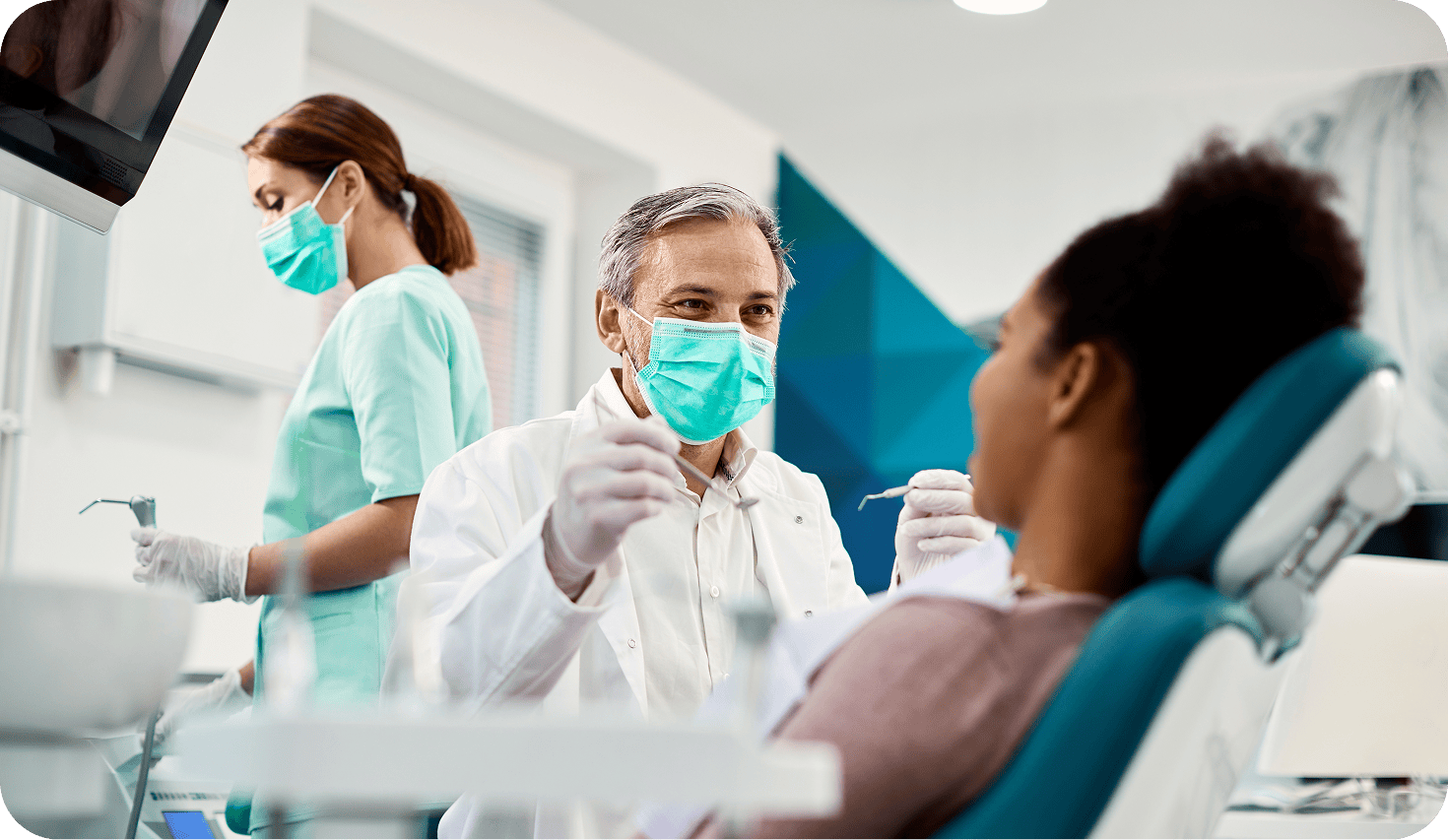


Scheduling regular dental visits to monitor your gum health and catch any issues early
Everything You Need to Maintain Your Oral Health
Flossing is an essential step in your daily oral hygiene routine. Regular flossing helps remove plaque and debris from between your teeth that brushing can’t, which can lead to the formation of tartar and gum disease like gingivitis. Not only does flossing every day help protect your gum health, but it can also make your teeth look brighter and allow you to regularly examine your mouth for any swelling or redness that could be signs of other health conditions.
At a minimum, you should floss at least once a day, but it's best to floss after every meal to promote good dental hygiene, prevent gum disease, and make your mouth feel cleaner.
With the right flossing products, like Oral-B Glide Pro-Health Comfort Plus Mint Floss, you can make flossing a convenient part of your daily oral hygiene routine.






